Performance Cops and Janitors
Last year I gave the keynote at OK200 about Firefox OS -- what it was, what it wasn't, and where to go from there. It went pretty damn well, or so I thought. I was followed by Lara Hogan from Etsy, whose presentation was so incredible it made my talk look like I describing MS Paint. And it was about an important but neglected topic: performance. The audience was hanging on her every word, as was I. Lara has written a book called Designing for Performance and has been nice enough to share an excerpt from Chapter 8, Changing Culture at Your Organization, with all of us!
 Performance improvements often begin as one person's voice within a company culture. You start to notice how other sites are making optimizations and improving their user experience through tweaks to perceived performance or total page load time. Then you start measuring how your competitors' sites fare in WebPagetest and comparing your site's performance to theirs. After beginning to learn about many of the easy performance wins that you could implement on your site, you start crafting improvements with little effort and tons of gains.
Performance improvements often begin as one person's voice within a company culture. You start to notice how other sites are making optimizations and improving their user experience through tweaks to perceived performance or total page load time. Then you start measuring how your competitors' sites fare in WebPagetest and comparing your site's performance to theirs. After beginning to learn about many of the easy performance wins that you could implement on your site, you start crafting improvements with little effort and tons of gains.
These are the individuals who often start out as performance cops or janitors. Cleaning up after other designers and developers becomes a routine chore for these individuals; sometimes they've taken this responsibility on themselves, or sometimes they were assigned these responsibilities. Either way, this road leads to burnout.
As time marches on, so many things will continue to create performance challenges for even the most stable site:
- New performance techniques emerge, like the recent implementation of picture.
- The site's hardware, brand, and code age.
- New designers and/or developers are hired.
- Existing designers and/or developers with great performance habits leave.
- Browsers continue to evolve.
- Web standards evolve, such as HTTP/2, which eradicates some existing performance constraints.
Having a dedicated team of people responsible for keeping track of these kinds of evolutions is important. A performance champion, or a team of performance champions, is an excellent tool for a company to lean on as the Web changes. But the responsibility for maintaining a high-performing site should not solely rest on the shoulders of these individuals. Everyone who works on the site should buy in to the importance of performance and understand what they can do to improve it.
If other designers and developers who shape the site aren't educated on performance, how can they make the best decisions about user experience? How can they weigh the balance between aesthetics and page speed? If they aren't empowered to make improvements, any performance champions will simply be playing cleanup after other people's work. Spending your time cleaning up other people's work (especially when it's preventable) is a one-way ticket to burnout.
A dedicated performance team can focus on:
- Giving lectures, lunch-and-learns, and workshops to educate others about performance
- Celebrating the good work of designers and developers on other teams who improve site speed
- Building tools to surface performance data in others' daily workflows to help them understand how they are directly impacting performance in their current work
- Defining baseline requirements for performance, such as a performance budget for each new project or a maximum page load time across the site
- Learning about emerging technology and new methods of improving performance
- Communicating publicly about changes in site performance and recent experiments and learnings, as shown in Figure 8-1
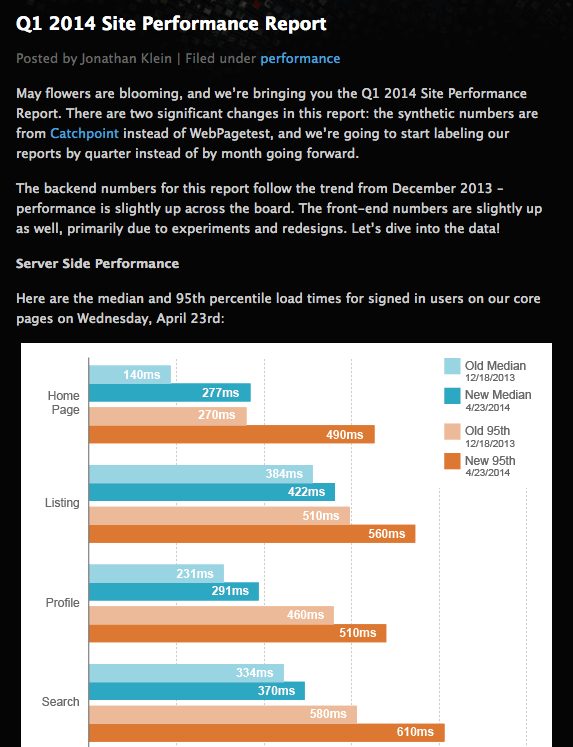
Figure 8-1. Etsy's performance report details load time for top pages and what changes contributed to the load time each quarter.
Having an individual or team care deeply about performance is important for all of the aforementioned purposes. These champions can stay on top of how performance is being handled sitewide; they can keep an eye on problem areas, look for areas to improve, and raise suggestions to the other people contributing to the site's design and development. But the work to be done to actually improve and maintain performance needs to be owned and shared across your organization, rather than lie with an individual or single team.
Read more about how to get upper management and fellow designers and developers to care about performance in the rest of Chapter 8 in Designing for Performance!
Designing for Performance by Lara Callender Hogan
http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920033578.do
ISBN 978-1-4919-0251-6
Copyright 2014 O'Reilly Media, Inc. All right reserved. Used with permission.

About Lara Hogan
Lara Callender Hogan is the Senior Engineering Manager of Performance at Etsy and the author of Designing for Performance. She champions performance as a part of the overall user experience, striking a balance between aesthetics and speed, and building performance into company culture.




